Bunion (Hallux Valgus)
What are Bunions?
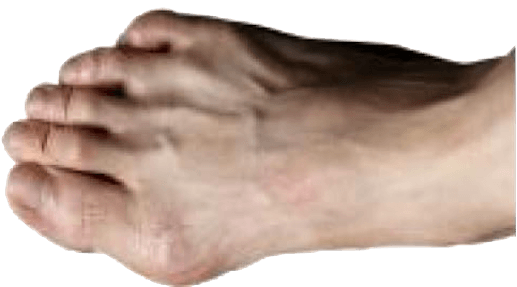
Bunions also know as Hallux Valgus is a bony protuberance and is a medical disorder of the foot and one of the most common reasons for painful toes.
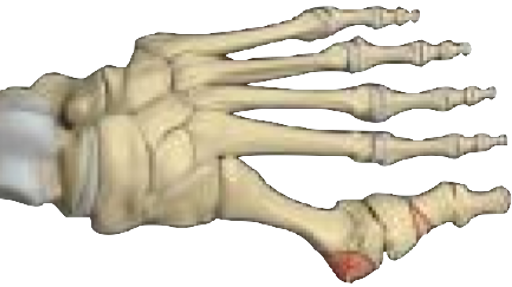
A misalignment of the bones in the feet resulting in the 1st metatarsal bone abnormally angles outwards resulting in a bony bump on the base of the big toe is known as a bunion.
Bunions appear on the external surface of the big toe when it angles toward the adjacent toe.
These conditions can become extremely painful over a long period of time.
Who Do Bunions Affect?
Bunions can affect anybody wearing improper shoes, people who are more likely to have arthritis and those having an inherited structural deficiency. Almost half of the women suffer from bunions, along with 25% of men.
They are more commonly found in elderly people over the age of 60.
How Do Bunions Occur?
Bunions most commonly occur due to external pressure that forces the big toe to fold over the smaller toes, turning inward. This results in the joint becoming larger and projecting outwards, resulting in the bunion formation.
Causes Of Bunions?
Although it is not clearly understood why bunions occur, possible causes include:
- Family history and genetics
- Arthritis (inflammation of the joints) including rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and gout
- Neuromuscular conditions such as cerebral palsy (affects movement and coordination)
- Connective tissue disorders such as Marfan’s syndrome (affects the connective tissues)
- Tight fitting shoes that are too tight, narrow or high heeled.
Bunions are common in women and tend to run in families (heredity).
Symptoms of Bunions
The symptoms include:
- Bony projection jutting outwards at the base of the joint of either the big toe or the little toe
- Tenderness and pain on touching or wearing shoes that are too tight
- Inflammation or redness around the affected joint
- Swelling
- Pain and tenderness around the big toe
- Turning of big toe towards the adjacent toe
- Change in the shape of the foot
- A bony mass at the joint surface of the big toe
- Pain and discomfort while walking
- Restricted movements of the big toe
Stages Of Bunions
With time and continued use of narrow uncomfortable shoes, bunions can become increasingly painful over time.
As the condition gets worse, it becomes more painful as the bump grows bigger in size. The big toe bends towards the next toe, changing the normal structure of the toes. A bump forms at the side of the big toe, making it difficult to walk or wear shoes.
How are Bunions Treated?
Bunions once formed, are permanent unless surgically removed.
Non Surgical Treatments for Bunions
Some non-surgical options that can be recommended for pain relief include:
- Wearing broad-toed shoes that fit properly to reduce the compression of the toes
- Using ice packs to reduce pain and swelling and getting adequate rest
- Using bunion pads, cushions and splints to protect and alleviate painful foot bunions
- Steroid injections to alleviate pain and swelling
In case the conservative approach still doesn’t result in pain relief, the doctor may recommend surgical options
Surgery for Bunions
to remove part of the bony projection or swollen tissue from the joint or fusing the bones of the affected joint to a better position permanently.
- Cheilectomy - Cheilectomy is required if arthritis of the big toe becomes painful and changing shoes and medication has been ineffective. In some cases, it is recommended early in the arthritis progression, in order to avoid complications later.
- Osteotomy - including Akin Osteotomy, Chevron Osteotomy and Scarf Osteotomy
The main purpose of this surgery is to improve the quality of life for an arthritis patient. The procedure provides instant and significant relief in almost all cases.
What If Bunions are Untreated?
A bunion can change the shape of your foot, make it difficult for you to find shoes that fit correctly.
If left untreated, bunions can become increasingly painful over time. Complication can include
- Bursitis (fluid-filled pad formation in the joints),
- Hammertoe formation and
- Metatarsalgia (tenderness and swelling in the ball of the foot).