Shoulder Reconstruction Surgery
What is a Shoulder Reconstruction Surgery?
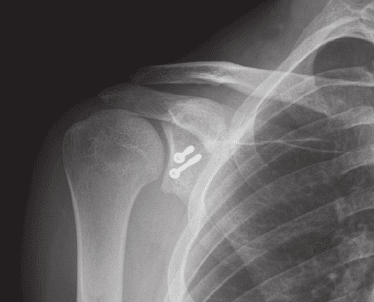
Shoulder reconstruction is required for patients with rotator cuff tear or labral tear to improve and restore function of the shoulder joint.
Shoulder reconstruction surgery involves repair of the torn ligaments so that they are able to move the shoulder joint in usual manner.
Types of Shoulder Reconstruction Surgery
Shoulder reconstruction surgery can be done
- Arthroscopically, involves use of smaller incisions and tiny instruments to perform the repair
- Open Surgery - involves larger incision over the shoulder to perform the repair.
Labrum Repair Surgery
Arthroscopic Labrum Repair Surgery is a type of shoulder reconstruction and stabilisation surgery.
This procedure can be considered for patients who have torn or stretched ligaments and other soft tissues in the shoulder that cause Shoulder Instability
Remplissage Procédure
The remplissage procedure can be added to the arthroscopic Bankart repair to increase shoulder stability. The procedure is reserved for individuals who have a large crush fracture in the back of the humeral head (Hill-Sachs Lesion), with minimal bone loss on the socket.
In the remplissage procedure, the fracture surface is freshened and anchors with sutures are used to tie the adjacent rotator cuff tendon into the defect. The humeral head compressed bone is excluded from the joint and can no longer engage over the front of the socket.
Shoulder Stabilisation surgery can also be performed arthroscopically, depending on the patient’s particular situation, with much smaller incisions. Rarely, arthroscopic surgery may need to be converted to open surgery to properly repair the damage to internal structures.
Bone Deficient Anterior Instability
In shoulder instability there can be loss of bone on the socket, humeral head or both. The failure rate for Arthroscopic Labral Repair in contact athletes with significant bone defects has been reported as high as 2/3.
For Bone Deficient Instability the Latarjet procedure is considered when a repair of the labrum does not correct the damage of the shoulder joint (ie: recurrent instability caused by a bony Bankart lesion)
The Latarjet procedure is a salvage procedure for difficult instability cases and is indicated for anterior shoulder instability that is . It is becoming a preferred method of treatment for anterior shoulder instability in certain situations.
relocating a piece of bone from the shoulder blade with an attached tendon to the shoulder joint.
Latarjet procedure is also considered in higher-risk individuals where a standard Bankart repair may have a higher risk of failing. This includes younger active patients, particularly involved in collision sports such as AFL
Dr Kalhor offers Laterjet procedure in lateral decubitus position, a position that will improve your graft positioning.
When is Reconstructive Shoulder Surgery Indicated
Reconstructive Shoulder Surgery is indicated for the following reasons:
- Failure of treatment such as immobilisation, prescription medicines, physical therapy, closed reduction or manipulation and occupational therapy fails to relieve the shoulder instability,
- Revision Surgery - Latarjet Procedure indicated
- Severe pain
- Shoulder instability or tendency to dislocate.
- Stiffness, Swelling, and Reduced range of motion
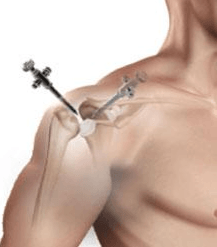
Steps of Latarjet Shoulder Surgery
The procedure is performed after appropriate diagnostic assessments, pre surgery checks and preparations are complete in hospital and takes typically less than 2 hours. The Latarjet Surgery involves as an open procedure +/- arthroscopy and involve:
- Performed under general anaesthesia with the patient in a semi-reclined or beach-chair position, it involves
- Small incisions are made from your shoulder blade towards the armpit.
- Muscles are moved to expose the coracoid process and its attached tendons.
- Coracoid process is freed of its attachments and along with the conjoined tendon is transected from its base.
- Holes are drilled into the transected coracoid process.
- Subscapularis muscle, which passes in front of the shoulder joint is split in line with its fibres.
- Capsule of the shoulder joint is entered and the glenoid is exposed and prepare to receive the coracoid.
- Transected coracoid with the conjoined tendon is passed through the separated subscapularis muscle and fixed to the glenoid rim with screws through the previously drilled holes to increase the glenoid surface and stabilize the joint.
- Conjoined tendon and subscapularis muscle provide additional stability by acting as a sling.
- Upon completion, the instruments are withdrawn, the incision is closed and covered with a sterile bandage.
Preparation for Reconstructive Shoulder Surgery
Once you and the doctor have decided that surgery is required, preparation is necessary to achieve the best results and a quick and problem free recovery.
- Infections - Treat any tooth, gum, bladder or bowel problems before surgery to reduce the risk of infection
- Smoking - Stop or cut down smoking to reduce your surgery risks and improve your recovery
- Weight - Consider losing weight (if overweight) before surgery
- Medications - Refrain from taking medications or dietary supplements that may increase your risk of bleeding - refer Medication Information
- Fasting - Depending on the type of anaesthesia used, your doctor may advise you to refrain from eating and drinking six to twelve hours before the procedure.
- Getting Home - You will not be allowed to drive yourself home after the procedure, so make arrangements for someone to pick you up. If you live alone, arrange for someone to check on you that evening or, ideally, to stay with you for the rest of the day.
- Loose Clothing - If you're having surgery, wear loose, comfortable clothing, such as baggy gym shorts and slip-on shoes, so you can easily undress and dress
Returning Home After Surgery
When you go home you need to take special precautions around the house to make sure it is safe. Your post operative plans should include:
- Detachable showerhead: You'll probably need to keep your incision dry for a while. Shower heads with detachable heads make it easier to avoid getting your incision wet.
- Shower chair: Because you can sit down while showering, a shower chair reduces your risk of falling. These are useful after surgery or if you're taking pain relievers that can make you dizzy or tired.
- Waterproof bandages or plastic bags with athletic tape: You may want to cover your incision with a large waterproof bandage or plastic bag with tape until your doctor says it is safe to do so.
- Pump soap: Using soap from a pump container makes showering with one arm easier.
Assess your home situation to ensure you have adequate home support in the first few weeks following surgery. If you live alone it may be necessary to arrange a package of community care to help during the first few weeks at home.
Reconstructive Shoulder Surgery Process
Reconstructive Shoulder Surgery Rehabilitation Program
Risks & Complications Associated with Reconstructive Shoulder Surgery
Surgical Follow Ups
How Risks Are Minimised
Get Moving Quickly
- Immobilization: Uses a sling to stabilize your shoulder for several weeks as your joint heals.
- Passive exercise: Relies on assistance and support of your physical therapist or a specific machine to move your arm gently starting a few weeks after surgery.
- Active exercise: Moves your shoulder and arm by using your muscles beginning up to three months following your surgery.
Don’t Resume Physical Activity Too Soon
Even if you are not in a lot of pain, you must still follow the doctor's instructions regarding when you can do certain things during your recovery period. Attempting to perform difficult exercises, activities, or sports that put strain on your shoulder may result in another injury. When you resume physical activities too soon, you may injure other parts of your body, such as your elbow or spine.
Receive Physical Therapy
On the day of your surgery, a physical therapist will see you a few hours after you arrive, and then twice a day for the next few days.
They will give you an exercise program to help you increase your range of motion. They will also teach you about safety through gait and transfer training as well as joint positioning.
Shoulder Surgery Exercises
To improve comfort and blood flow, the doctor will most likely instruct you to straighten and bend your elbow, perform gentle pendulum motions, and clench and unclench your fist on a regular basis.
How Can I Minimise Post Operative Complications
Blood clots (DVT or PE)
All patients receive a number of treatment measures to reduce the risk of blood clots. These include injections of heparin during and after surgery,
As a result of these measures, we have never had a patient develop a deep venous thrombosis. Any patient who is at high risk of a blood clot (such as a history of blood clots or clotting disorders) may be asked to continue heparin (Clexane) injections for 10 days after the surgery in addition to the other measures. This can be done at home, and we will show you how.
What Are the Consequences of Surgery?
Sometimes the potential risks and consequences of your surgical procedure need to be weighed against the benefits of a successful surgical outcome.
Like most surgery these benefits can include:
- Freedom from pain
- Increase movement
- Greater Flexibility,
- Maintained Independence
- Improved outlook, and
- Longer more enjoyable life
Although the recurrence of the presenting problem is not very common, after surgery, you would need to follow preventive measures.